
How the Consortium Blockchain Works
September 25, 2019
Corda and Real Businesses Built on Top of This Framework
August 23, 2019
Imagine that you’re the owner of a new application and you’re just coming to the market. Take Instagram for example, they started on Mac-mini on only 1 server but they had to move quickly to ABC because the capacity required a swift upgrade as it grew with 50,000+ users per day.
And the next thing you realize is that people develop a genuine interest in your application. But, if you trigger such widespread interest in an application, it’ll generate vast quantities of data. So one has to find a solution to keeping high throughput along with the exponential growth.
One can have 2 databases to decrease the load and then add 10 more. However, do we need to store full copies of files on each of them? That’s when sharding comes in.
In this guide, I’ll explain the basic concept of sharding, when sharding is necessary and what sharding is in relation to the blockchain technology.
Let’s get started.
According to TechTarget, the general definition of “sharding” is:
“Sharding is a type of database partitioning that separates very large databases the into smaller, faster, more easily managed parts called data shards. The word shard means a small part of a whole.”
Simply put, if you “shard” a database it involves splitting up one big piece of data into multiple, much smaller database and a very fast way to detect which shard stores particular information. These “smaller databases” can then be shared and divided across several servers hosting these files which will make both throughput and performance very efficient.
Another term for sharding is horizontal partitioning but there’s also an option for vertical partitioning. The difference between these two is related to the traditional table view of a database.
In other words, when you split a database vertically, you slice different tables or entities to separate databases. While horizontally splitting a database means that you slice the rows of a particular table in multiple databases.
The blockchain has many enthusiasts who truly believe that the technology behind the blockchain is going to be part of everyone’s life in the (near) future and it’s going to reshape many of the systems we currently use.
We have elected to put our money and faith in a mathematical framework that is free of politics and human error,” says Tyler Winklevoss, a founder of Winklevoss Capital Management.
Think about borderless payments without fees, interchangeable currencies, no centralized third parties (authorities, banks, and other institutions) to verify the movement of goods or funds and much more.
I do believe that the blockchain technology has the potential to be implemented in various industries and replace current systems. However, there are quite a few roadblocks up ahead that have to be dealt with in order to make some serious steps forward. One of these roadblocks is the scalability issue that many cryptocurrency developers are currently facing.
As of right now, for example, Bitcoin has the ability to handle 3-7 transactions per second, while Ethereum has the ability to handle 12-30 transactions per second.
Imagine if Ethereum would replace TransferWise, Neat or Revolut right now, it doesn’t take a genius to see that this would be a massive problem. It might take weeks for your transaction to be validated. It comes to no surprise that developers are working on potential solutions in order to solve this roadblock. What’s more, keep in mind the escalating number of data which requires a range of technical solutions.
Which brings us to “sharding.” In short, sharding is designed to deal with such scalability issues. And, Ethereum is doing just that by walking down a new path by looking into the possibilities of sharding the Ethereum network.
The current validation process of Ethereum is based on a concept called Proof of Work (PoW). This concept challenges miners to solve complex cryptographic puzzles by using a lot of computational power.
By doing so, the miners generate the correct key to create a new block, which holds transactions and other data. The blocks are chained together, storing both the new hash as well as the hash of the previous block. This is a very safe validation process but it also takes up a lot of time.
Sharding can also offer a solution when it comes to the validation process of new transactions within a blockchain network. Whereas PoW requires the validation of the entire network, sharding can create a small subset of nodes (participants in the network) to carry out the validation process of the transactions.
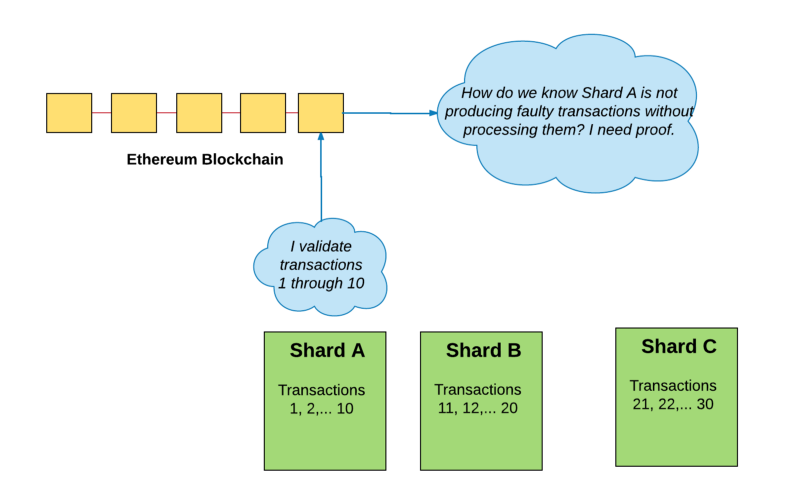
You could compare this process to real life states and provinces in countries. Countries do this so that the local governments can make decisions on a lower level, which is way more efficient. Ethereum could be sharded following the same concept.
That means that every subset of nodes will have their own dedicated miners to solve the calculations, generate new hashes and in return validate transactions within a node subset. By doing so, the ability to handle way more transactions in a shorter amount of time would improve significantly.
In addition, the network would be more flexible, simply because the number of transactions in a subset of nodes would be a lot smaller in comparison to the entire network that is currently stored on nodes, which also addresses the scalability issue.
The concept of validation transactions would remain the same, however, it’s on a much smaller scale. So, security-wise, it wouldn’t really suffer.
The DLT market is rapidly expanding and, as many people expect, the blockchain technology will shape systems and infrastructures in the future.
However, the technology still requires a lot of innovations and improvements before it’ll reach a state of real influence. When these networks keep growing, sharding will become more essential in order to solve the scalability issues that many of these blockchain technology applications are facing.
This is a guest post submitted by Bill Hess from PixelPrivacy. Ideas in this post reflect personal views of the author. If you want to submit your own guest post, please send your topic to blockchain@intellectsoft.net
Bill here from PixelPrivacy.com. My blog is all about making the world of online security accessible to everyone. I pride myself in writing guides that I’m certain even my own mom could read! Be sure to head over to my blog if you’re interested in keeping your private information just that: Private!


