
How the Consortium Blockchain Works
September 25, 2019
Corda and Real Businesses Built on Top of This Framework
August 23, 2019
Many of you have heard the word “Hyperledger” in the context of the buzz around blockchain. Hyperledger is a blockchain framework in the form of a simple, flexible, and distributed digital ledger. In this article, we are going to describe all of its ecosystem, including private and public variants of the technology. We recommend getting familiar with some blockchain fundamentals first, or you can dive straight in.
Table of contents:
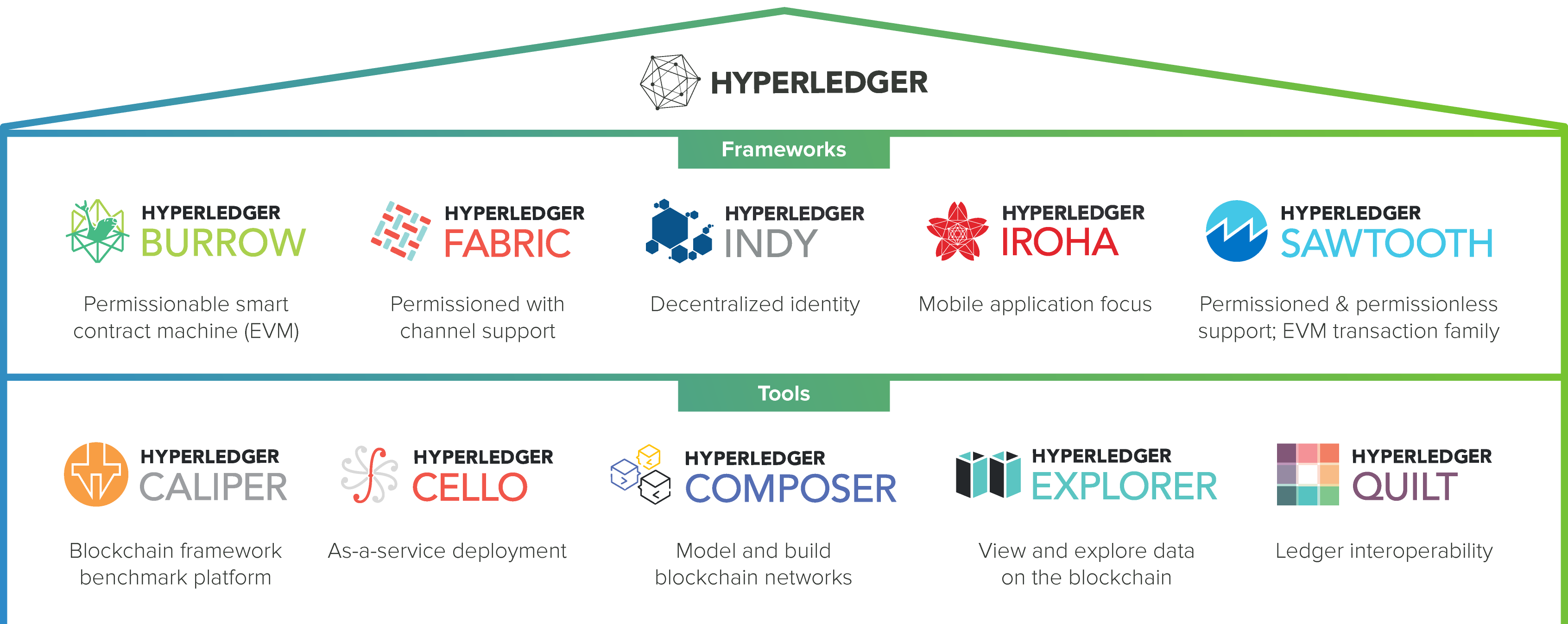
The Greenhouse: Hyperledger Framework Ecosystem. Credits: Hyperledger
Hyperledger is an open source project established to assist enterprises around the world deliver on the promise of blockchain for more secure, more reliable, and more streamlined interactions. It is a global collaboration, hosted by The Linux Foundation, and includes leaders in finance, logistics, Internet of Things, manufacturing, and technology.
Hyperledger aims to advance cross-industry blockchain technologies. So far, it has one of the largest blockchain developer communities and allows them to utilize the technology for designing data-sharing networks, micro-currencies, operating systems for marketplaces, and decentralized digital communities.
The following are key characteristics of Hyperledger:
“Hyperledger Fabric and Ethereum are complementary not competitive to each other”,— Hyperledger Project Executive Director Brian Behlendorf
What is more, it’s widely agreed that blockchain developers who work on Hyperledger only win from it: the project is used by dozens of enterprises and the framework itself strives for interoperability with other blockchains. The greenhouse structure of Hyperledger encourages specialization, which yields better productivity. Therefore, participants who specialize in similar areas aren’t competing against each other but instead can join forces.
It has the potential to vastly reduce the cost and complexity of getting things done in the real world. As of publication date, there are 5 types of Hyperledger framework and 5 tools within the ecosystem.
IBM’s Christopher Ferris on Hyperledger Ecocystem and its use cases.
Credits: “Blockchain: Rethink Trust” Conference 2018
Hyperledger Burrow is a permissionable smart contract machine. It is a modular blockchain client that executes a permissioned smart contract code, usually written in Solidity or Viper.

Type: Permissioned Smart Contract Application Engine
Status: Incubation
Real world examples: N/A
Its first version saw the world in December, 2014 under the name ErisDB. Burrow is owned and developed by Monax and is now under the umbrella of Hyperledger. It works with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and can turn loan applications into smart contracts as well as seamlessly attach them to strong identities.
Hyperledger Fabric was intended as a foundation for developing applications or solutions based on a modular architecture. It makes components, such as consensus and membership services, plug-and-play.

Type: DLT, Smart Contract Engine
Status: Active
Real world examples:
Fabric is perhaps the most recognized blockchain framework from the Hyperledger family. According to Christopher Ferris, “few open source blockchain projects have a development community as diverse and large as Hyperledger Fabric.” He adds that there isn’t a “most suitable use case” since Fabric was invented to support a broad range of enterprise applications, from finances to supply chain to insurance and to healthcare.
Fabric is a private and permissioned blockchain and has no cryptocurrency, therefore, transactions are free. While anybody can join a public blockchain, only members enrolled through a Membership Service Provider can be part of the Hyperledger Fabric private blockchain. Furthermore, Fabric does not rely on Proof-of-Work to ensure consensus but instead offers a pluggable architecture, where a client can define his own consensus algorithm.
Hyperledger Fabric Explainer. Credits: Hyperledger
Importantly, Fabric implements an “execute – order – validate” model of transaction processing that both supports a variety of consensus algorithms and appears to be more efficient than the common “order – execute.” This is due to the fact that the transaction can be confirmed as soon is it has been committed to a single node since the validation step is deterministic: the transaction will be either validated or not across the network.
Today, Hyperledger Fabric supports Go and Javascript chaincode and has a variety of application developer SDKs (software development kit) in Go, Java, and Python. There are also experimental versions of Java and EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) chaincode capability that developers are hopeful to release this fall. It will let Java and Solidity developers create smart contracts for Hyperledger Fabric.
Hyperledger Indy is a distributed ledger that provides tools, libraries, and reusable components for creating and using independent digital identities rooted in blockchain for interoperability.

Type: Distributed Ledger and Utility Library
Status: Incubation
Real world examples: N/A
Since distributed ledgers are immutable and append-only, it is crucial to carefully consider foundational components for ledger-based identity, including performance, scale, trust model, and privacy. Indy helps to streamline credentials and strives to improve privacy by design, especially on the scale of a global public identity ledger.
Indy shares some features with available blockchain-based identity solutions like Blockstack and Uport but does not require PoW as they do. This makes Indy more flexible, cost-effective, and practical since the transaction cost is zero and the framework can scale to fit any enterprise demand.
Hyperledger Iroha is a business blockchain framework that makes the implementation of the distributed ledger technology into infrastructural projects easy and simple.

Type: DLT, Smart Contract Engine, Utility Libraries
Status: Active
Real world examples: N/A
There are only a few moments which differentiate this particular framework from others: it has a unique consensus algorithm entitled “Yet Another Consensus and the BFT ordering service.” Also, it can manipulate accounts using only a small set of fast commands and queries. The Iroha participants are simultaneously validation nodes that can distribute half-signed transactions over the Gossip protocol which represents multi-signature transactions.
Together with the powerful role-based permission model that leverages grant capabilities, the end-user applications are claimed to be endless. Applications powered by this framework can be written in Python, Java, JavaScript and C++ as well as for the Android and iOS mobile platforms.
Hyperledger Sawtooth is a modular platform for building, deploying, and running distributed ledgers and includes a different consensus algorithm, Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET), which addresses large distributed validator populations with minimal resource consumption.

Type: DLT, Smart Contract Engine
Status: Active
Real world examples:
In combination with IoT sensors, Hyperledger Sawtooth can track the ownership and journey of products from the origin place to the end consumer. It provides a reliable and powerful way to support post-trade activities. What is more, Sawtooth helps to build complex rules while utilizing a preferred language and exposing only the functions appropriate to the context. This makes it a safer smart contracts environment with many participants.
Hyperledger Caliper is a blockchain benchmark tool that allows users to measure the performance of a specific blockchain implementation with a set of predefined use cases.

Type: Tool
Status: Incubation
Real world examples: Hyperledger internal usage
Hyperledger Caliper will help to assess and produce reports regarding the following performance indicators: TPS (Transactions Per Second), transaction latency, resource utilization, and others. Therefore, the Caliper tool will help other Hyperledger projects as they are in the process of development, and serve as a reference point to suit a user’s specific needs.
Hyperledger Cello is going to bring the on-demand “as-a-service” deployment model to the Hyperledger ecosystem and reduce the effort required for creating, managing and terminating blockchains.

Type: Utility
Status: Incubation
Real world examples: N/A
Cello offers a multi-tenant chain service efficiently and automatically on top of various infrastructures such as bare-metal server, virtual machine, and more container platforms. Cello aims to become a necessary tool for fine-tuning various blockchain projects.
Hyperledger Composer is a collaboration tool for designing and deploying blockchain business networks.

Type: Tool
Status: Incubation
Real world examples: N/A
Composer offers business-centric abstractions, including sample apps with easy to test devops processes to create sturdy blockchain solutions that reach alignment across business requirements with technical development. Composer will accelerate the development of smart contracts and their deployment across a distributed ledger.
Introduction to Hyperledger Composer. Credits: Hyperledger
Hyperledger Explorer allows one to view, invoke, deploy or query blocks, transactions and associated data, as well as any other network information, chain codes and other relevant information saved in the ledger.

Type: Utility
Status: Incubation
Real world examples: For now, internal use only
Hyperledger Quilt brings interoperability between ledger systems using the implementation of ILP, which is in most cases a payments protocol and is created to transfer value across distributed ledgers and non-distributed ledgers.

Type: Tool
Status: Incubation
Real world examples:
The Interledger protocol offers atomic swaps between ledgers, including the non-blockchain or non-distributed ledgers, and a single account namespace for accounts within each ledger.
Quilt consists of:
Interestingly, NTT Data and Ripple first contributed to Hyperledger Quilt. Nowadays, the Linux Foundation employs both the Java (Quilt) and JavaScript (Interledger.js) Interledger options.
Hyperledger development with Arnaud Le Hors. Credits: “Blockchain: Rethink Trust” Conference 2018
For more details read the Hyperledger white paper or contact us.
The first mover advantage and a constellation of partnerships with enterprises and consortia secure Hyperledger framework a solid place in the blockchain development space. For developers, it means a clear focus for advancing their knowledge. For businesses, it is a no-brainer choice for their decentralized application or a distributed solution that requires transparency, immutability, and high-yield efficiency.
As a result, we are going to witness new work and releases to improve the interoperability of the Hyperledger ecosystem. It is also possible that additional Hyperledger frameworks will emerge in the near future to meet the demand for blockchain development and even more use cases.
Looking for blockchain development? Get in Touch with Intellectsoft Blockchain Lab!


